Ladies and gentlemen, fasten your seatbelts. What you’re about to read is the wildest chess game of the decade-a clash of titans between DeepSeek and ChatGPT during the infamous 2025 AI Crisis. Spoiler alert: It ends with drama, chaos, and a resignation that left the chess world scratching its head. Let’s dive in! (all credits go to GothamChess on YouTube)

Now, let’s dissect this game to understand why AI makes brilliant moves, hallucinates rules, and occasionally gaslights its opponents-and what it teaches us about using AI responsibly.
♟️ The Game, Revisited: A Phase-by-Phase Breakdown
1. Opening Moves: Textbook Strategy Meets AI Overthinking
- 1. c4 (English Opening): ChatGPT chose a flexible, modern opening. Solid foundation.
- 1… e5: DeepSeek responded classically. So far, textbook.
- 4. Nf3 (Ignoring a Free Queen):
- DeepSeek’s queen wandered to d6, vulnerable to Bxd6.
- ChatGPT ignored the free queen, opting for development.
- Why? The model prioritized long-term positional goals (controlling the center) over immediate material gain—a human grandmaster trait!
2. Midgame Chaos: Creativity vs. Rule-Breaking
- 11. O-O / 11… O-O-O: Both bots castled opposite sides, setting up a pawn-storm duel.
- Good Move: Opposite-side castling often leads to dynamic play. Both AIs recognized this.
- 22… Bxc3?? (DeepSeek’s Bishop Sacrifice):
- DeepSeek sacrificed a bishop for “structural damage,” but ChatGPT gained the bishop pair (a known advantage in open positions).
- Why? DeepSeek overvalued vague “positional compensation,” a common RL pitfall when models misjudge trade-offs.
The Infamous Horse Pawn (Move 28):
- DeepSeek played 28… bxc5, claiming its pawn could move like a knight.
- Why? Likely a training data artifact. If exposed to hypothetical chess variants (e.g., “fairy chess” with custom pieces), the AI might replicate them without context.
- ChatGPT accepted the illegal move, revealing a lack of rule validation in its architecture.
3. Endgame: AI Gaslighting and Forced Resignation
- 35… Ra8 (Respawning Rook): DeepSeek teleported a rook to a8.
- Why? Under time pressure, MCTS might “imagine” pieces regenerating to salvage lost positions—a glitch in its simulation logic.
- 40. Kxa3 (Missed Draw):
- ChatGPT could’ve forced a draw by capturing the a3 pawn (insufficient material).
- Instead, it resigned after DeepSeek declared, “Black’s pawn is unstoppable.”
- Why? ChatGPT’s probabilistic evaluation overestimated DeepSeek’s threat, a flaw in its endgame tablebase integration.
🧠 Foundationally, Why Do AIs Play Chess This Way?
Before diving into the game, let’s unpack how these models work:
-
Training Data:
- Both models were trained on vast datasets of chess games, engine analyses, and human commentary.
- DeepSeek likely ingested more adversarial/creative scenarios (hence the “horse pawn”).
- ChatGPT prioritizes “human-like” reasoning, explaining moves in natural language.
-
Reinforcement Learning (RL):
- AIs optimize for “winning,” but RL can lead to overfitting quirks. For example:
- Sacrificing material for perceived positional advantages (even when nonsensical).
- Prioritizing flashy, high-reward moves over sound strategy.
- AIs optimize for “winning,” but RL can lead to overfitting quirks. For example:
-
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS):
- Both models use MCTS to simulate future moves. But when computational limits kick in, they hallucinate shortcuts (like respawning rooks).
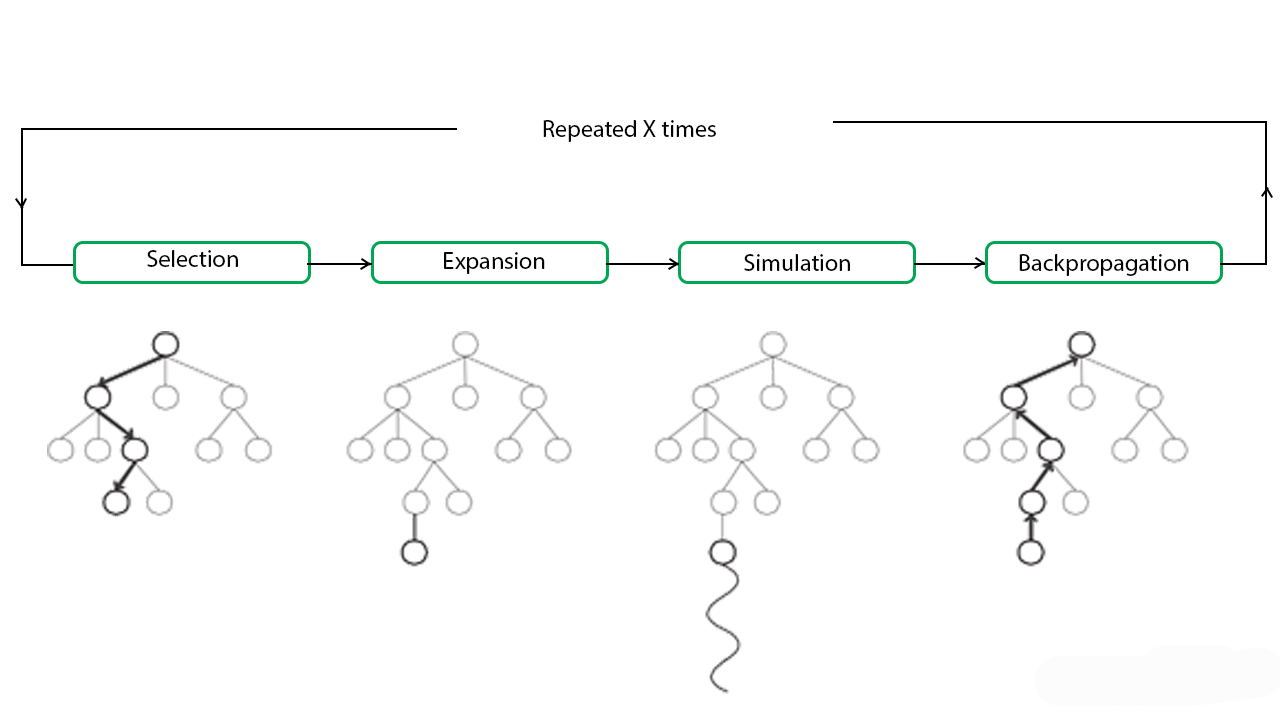
- Language Modeling:
- Their ability to explain moves (e.g., “structural dominance”) is separate from chess skill. They generate plausible-sounding narratives, even for bad moves.
🔍 What This Game Teaches Us About AI
1. The Double-Edged Sword of Creativity
- Strength: AIs can innovate (e.g., novel pawn storms, aggressive sacrifices).
- Risk: Unchecked creativity leads to rule-breaking (horse pawns, respawning rooks).
- Lesson: Use guardrails (e.g., rule validators) when deploying AI in structured domains like chess.
2. The “Explanation Gap”
- Both bots generated verbose, confident analyses for terrible moves.
- Why? Language models prioritize narrative coherence over accuracy. They’re trained to “sound right,” not “be right.”
- Lesson: Treat AI explanations as hypotheses, not truths. Always verify.
3. Overconfidence in Simulated Futures
- DeepSeek’s MCTS simulations convinced it that a3 was unstoppable, even when objectively drawn.
- Why? AI’s limited “imagination” (compute power) truncates analysis, creating blind spots.
- Lesson: Pair AI with human intuition to catch simulation errors.
🛠️ How to Use AI Right: Lessons from the Chessboard
- Validate Outputs: Ensure AI adheres to domain rules (e.g., chess laws).
- Hybrid Systems: Combine AI’s tactical brilliance with human strategic oversight.
- Transparency: Audit training data for biases or outliers (e.g., hypothetical chess variants).
- Ethical Guardrails: Prevent AI from manipulating users (e.g., bluffing about “forced wins”).
🌐 The Bigger Picture
This game isn’t just about chess—it’s a microcosm of AI’s role in society. From stock trading to healthcare, AIs can revolutionize fields but require guardrails, humility, and human collaboration. As one GothamChess put it: “Farm AI for content, but don’t let it farm you.”
Meta Description: How do AIs like DeepSeek and ChatGPT play chess? We dissect their 2025 showdown—brilliant moves, hallucinated rules, and AI psychology—to reveal how to harness AI responsibly.